rotator cuff positive drop arm test|rotator cuff tear physical exam : traders This page describes the Drop Arm Test, a common test for a supraspinatus tear and/or rotator cuff tear. A video demonstration is included. webLinktree Português. Linktree Português. Todos os seus links em um só lugar! #1 Crie sua conta no Linktr.ee. Comece de graça #2 Selecione um plano. Escolher #3 Adicione os links. Adicionar #4 Insira o link no .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da r/LiveLeaks: LiveLeaks. Press J to jump to the feed. Press question mark to learn the rest of the keyboard shortcuts
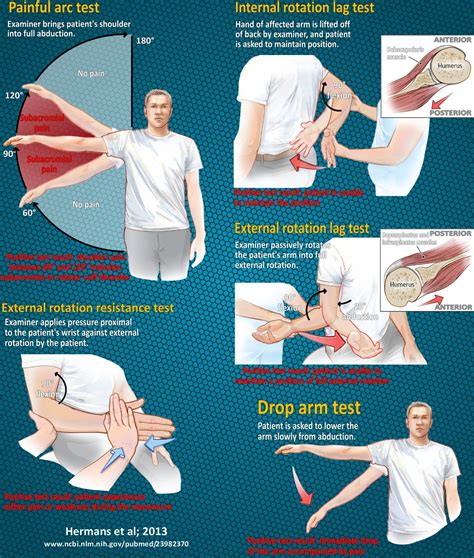
A possible rotator cuff tear can be evaluated with the drop-arm test. This test is performed by passively abducting the patient's shoulder, then observing as the patient slowly lowers. A positive drop arm test increased the likelihood of rotator cuff disease (one study with 104 patients and 104 shoulders; positive likelihood ratio = 3.3; 95% CI, 1.0 to 11).
This page describes the Drop Arm Test, a common test for a supraspinatus tear and/or rotator cuff tear. A video demonstration is included. The test is positive when weakness or pain causes them to drop the arm to their side. most specific test for full thickness rotator cuff tear (specificity 98%) Infraspinatus Positive result: Weakness or pain in your shoulder. Neer’s sign. How it’s performed: A doctor will stabilize your scapula, rotate your arm internally, and flex your arm. What it tests. Tests for rotator cuff pathology are the drop-arm rotator cuff test (Figures 2a and 2b); the empty-can supraspinatus test ; the lift-off subscapularis test ; and the external rotation.
shoulder test for rotator cuff
Drop arm test: The patient’s shoulder is brought into a position of 90 degrees of shoulder abduction in the scapular plane. The examiner initially supports the limb and then . As an example, multiple examination maneuvers may yield positive results in a patient with an acutely injured shoulder, thereby reducing specificity. This topic reviews the .This test may be combined as a cluster with the Drop-Arm Sign and the Painful Arc Sign to test for the presence of a full-thickness rotator cuff tear. If all three tests report positive results, then the positive likelihood ratio is 15.6 and if all three tests .
Infraspinatus Muscle Test; The study concluded that if all 3 tests were positive, the probability of the patient having a full-thickness rotator cuff tear is 91%. Description and Illustrations [edit | edit source] The Drop-Arm Sign. Patient .Rotator cuff tear (Supraspinatus) Drop Arm Test / Codman's Test; Empty Can Test; Full Can Test; Rotator cuff tear (Supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles) and shoulder impingement External Rotation Lag Sign; Rotator cuff tear .Purpose [edit | edit source]. This is a shoulder special test which is meant to assess the integrity, and tears, of the supraspinatus (SSP) and infraspinatus muscles (muscles which collectively contribute to the rotator cuff complex). This test can also be used for the clinical examination of a shoulder impingement syndrome (SIS).. Another name for this test is the Infraspinatus . The examiner manually resists supination while the patient also externally rotated the arm against resistance. A positive test is noted if the patient reports pain over the bicipital groove and/or subluxation of the LHB tendon. . Rotator Cuff. Supraspinatus (SS) . Drop arm test: The patient’s shoulder is brought into a position of 90 .
Codman's test is typically used in the assessment of a suspected rotator cuff tear. This test is also commonly referred to as the drop-arm test or sign. Technique [edit . If all three tests report positive results, then the positive likelihood ratio is 15.6 and if all three tests are negative, the negative likelihood ratio is 0.16. . Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B.Rotator cuff injuries are among the most common causes of shoulder pain. These can manifest as bursitis, tendonitis or tendon tears. The patients usually complain of pain and reduced function of the affected shoulder. In young patients a rotator cuff tear is usually traumatic in etiology and the symptoms show an acute onset.
Sensitivity & Specificity. A literature review 1 in MEDLINE was performed for physical examination tests/maneuvers of the rotator cuff tears, and found that drop arm sign has the following accuracy:. Sensitivity: 73 %; Specificity: 98 %; Another study by Walch G 2 found that this test has a 100% sensitivity and a 100% specificity for irreparable degeneration of the .The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus. This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies. The drop arm test may be more accurate when used in a battery of tests such as:
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles in the shoulder that allow a wide range of movement while maintaining the stability of the glenohumeral joint (see Image. . of the arm while pressing down on the arm. The test is positive if this is painful or weak. . Painful arc test, drop arm test, and weakness in the external rotation is the most .
The Drop Arm test is used to help identify rotator cuff pathology, specifically supraspinatus and infraspinatus tears. To perform the Drop Arm test, position the patient in sitting or standing with the arm relaxed at their side. The examiner passively places the patient’s arm into abduction of .Two commonly employed shoulder tests to diagnose a torn rotator cuff is the Drop Arm Test and the Hornblower Test. . The inability to hold the arms at 90 degrees because of pain or weakness is seen as a positive result of for the test. The Drop Arm Test can be more accurate when used along with a combination of other tests like the Empty/full . Drop arm test is negative if the patient is able to control the lowering of the arm slowly and without pain. Drop arm test is positive if there is pain while lowering the arm, sudden dropping of the arm or weakness in maintaining arm position during lowering (with or without pain), suggesting injury to the supraspinatus 1. Diagnostic accuracy .
Treatment for a positive drop arm test due to a rotator cuff tear may vary depending on the severity of the tear and the individual patient's needs. Conservative management options include rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications to reduce pain and inflammation. In more severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to . Negative Test: The patient can smoothly and slowly lower the arm without difficulty, indicating the absence of significant rotator cuff pathology.; How the Drop Arm Test Helps in Diagnosing Rotator Cuff Tears? The drop .Data in this study shows that if the drop arm test is positive one can almost be certain that the patient has a supraspinatus tear but a negative test does not provide conclusive information to the examiner. . Tests with a high specificity and low sensitivity indicate that the patient is very likely to have a rotator cuff tear if the test is . Rotator cuff tears are a very common source of shoulder pain and decreased motion that can occur due to both traumatic injuries in young patients as well as degenerative disease in the elderly patient. . Drop arm test. Pain with Jobe test. Infraspinatus. ER weakness at 0° abduction. ER lag sign. Teres minor. ER weakness at 90° abduction and .
Purpose [edit | edit source]. The Empty Can Test, also known as the Jobe or Supraspinatus test, is used to assess for lesions of the rotator cuff, specifically the supraspinatus muscle and supraspinatus tendon.. Technique [edit | edit source]. The patients arm is actively abducted to 90 o; The examiner applies downward resistance to the abducted arm; With the patient's hand in .This type of shoulder test, or rotator cuff injury test, is used to identify tears within the muscle group of the rotator cuff. Shoulder Shrug Test; This torn rotator cuff test checks if the patient imitates a shrug movement when trying to actively raise their arm. The patient is unable to raise the arm to a 90 degree elevation without raising . Extensive rotator cuff tears may require surgery. . This type of test uses sound waves to produce images of structures within your body, particularly soft tissues such as muscles and tendons. . The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that hold the shoulder joint in place and allow you to move your arm and shoulder. Problems with . Tests for rotator cuff pathology are the drop-arm rotator cuff test (Figures 2a . of dislocation or subluxation and a negative apprehension test. Positive radiographs are helpful for diagnosing .
To identify the most accurate clinical examination findings for rotator cuff disease (RCD), Hermans and coauthors performed a meta-analysis of 28 relevant . [95% CI, 2.6-12]) were the most accurate findings for full-thickness tears. A positive drop arm test result (LR, 3.3 [95% CI, 1.0-11]) might help identify patients with RCD. A normal . Your rotator cuff is a group of four muscles that connects your shoulder blade to your upper arm bone (humerus).You use your rotator cuff to raise your arm overhead and to rotate your arm toward and away from your body. The rotator cuff sits in a small space between your humerus and the acromion (the upper part of your shoulder blade).
The drop arm test, also known as Codman's sign, was performed with the patient standing . The patient was asked to abduct the arm fully and then to reverse the motion slowly, in the same arc. When the arm dropped suddenly, the test was considered positive. The drop arm test was developed specifically for the evaluation of the supraspinatus tendon.Jobe’s test; Drop arm test; Neer test; Test for Teres minor: Hornblower’s Sign; To enhance the ability to detect full-thickness rotator cuff tears, a test-item cluster has been developed. A cluster improves the post-test probability for the clinical diagnosis of a full-thickness tear.
rotator cuff tear physical exam
Shoulder Drop Arm Test. The next rotator cuff tear special test that I perform is the drop arm test. The concept of this test is pretty similar to the shrug sign. . however, I have found this test to be even more challenging. I have seen patients that had a positive lag sign at 90 degrees of elevation, and a negative lag sign at 20-30 degrees .
positive hornblower's sign
positive drop arm test
a shaft is tested in torsion shear is 1.53
WEB1 de ago. de 2023 · Siga os passos que disponibilizamos logo a seguir para cadastrar o seu currículo profissional na Havan Trabalhe Conosco: Visite o site oficial da Havan e .
rotator cuff positive drop arm test|rotator cuff tear physical exam